這一章先討論了 PKI ,然後引用了海綿寶寶的例子來做說明,還蠻有趣的,一看就能懂。
接著是提 symmetric key algorithm,Android 內支援的有四種:AES, twofish, blowfish, camellia,不管是用哪一種,程式的方式相當一致,就是 KeyGenerator.getInstance("AES"); 這邊帶的參數不一樣。
然後是講到 padding,symmetric key algorithm 是以區塊為單位去做加密,因此會有 padding 問題。什麼是 padding?所謂的 padding 就是未滿資料區塊大小時所要填入的值,像 zero-padding 就表示是填 0;未指定的話,Android 是使用 PKCS5 padding。
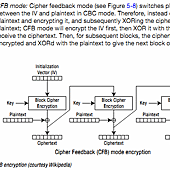
再來就是區塊的處理,這邊介紹了 ECB, CBC, PCBC, CFB, OFB 這幾種 mode,看圖會比較容易懂。ECB 就是最簡單的處理,一塊就加密一次,所以 hacker 要破解時,就不用管前後文,直接針對某一塊去暴力破解就好,為了增加破解的複雜度,就有了後面幾種 mode,基本就是利用前一段加密過程所產出的東西來當作這一段的資料之後再加密。



接著介紹 Android 的儲存機制,Android 的儲存機制有 Shared Preferences, Internal Storage, External Storage, SQLite databases, Network connection。Shared Preferences 實體是 .xml 檔,真正的位置是在 /data/app/app 的資料夾下,這裡說可以設為 MODE_PRIVATE, MODE_WORLD_READABLE, MODE_WORLD_WRITABLE, MODE_MULTI_PROCESS。Internal Storage 的真正位置跟 Shared preferences 一樣,只是就不限於 xml。External Storage 則是在 SD Card 上。SQLite database,列出來的意思不知道是什麼,實際上這取決於放在哪裡。Network connection 的話,就是連線,一般最好就是用 SSL。列出機制以後,就是一堆範例程式。
Shared preference 是用 getSharedPreferences();Internal Storage 是用 context.openFileOutput()/context.openFileInput() 直接開檔做讀寫;SQLite Database 則要建立類別繼承 SQLiteOpenHelper ,複寫必要的函式以建立資料表格、做 CRUD 。作者是說,一般直接讀寫的情況比較少,他自己是都用 shared preference / sqlite database 比較多,操作比較方便。
章節最後是綜合應用,作者建立了一個 KeyManager 用來存放 key,Crypto 則用來作加解密:
使用的時候直接用 Crypto 即可,Crypt 內部會自動去建立 KeyManager,然後使用。

接著是提 symmetric key algorithm,Android 內支援的有四種:AES, twofish, blowfish, camellia,不管是用哪一種,程式的方式相當一致,就是 KeyGenerator.getInstance("AES"); 這邊帶的參數不一樣。
public static byte[] generateKey(byte[] randomNumberSeed) {
SecretKey sKey = null;
try {
KeyGenerator keyGen = KeyGenerator.getInstance("AES");
SecureRandom random = SecureRandom.getInstance("SHA1PRNG");
random.setSeed(randomNumberSeed);
keyGen.init(256,random);
sKey = keyGen.generateKey();
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
Log.e(TAG,"No such algorithm exception");
}
return sKey.getEncoded();
}
然後是講到 padding,symmetric key algorithm 是以區塊為單位去做加密,因此會有 padding 問題。什麼是 padding?所謂的 padding 就是未滿資料區塊大小時所要填入的值,像 zero-padding 就表示是填 0;未指定的話,Android 是使用 PKCS5 padding。
再來就是區塊的處理,這邊介紹了 ECB, CBC, PCBC, CFB, OFB 這幾種 mode,看圖會比較容易懂。ECB 就是最簡單的處理,一塊就加密一次,所以 hacker 要破解時,就不用管前後文,直接針對某一塊去暴力破解就好,為了增加破解的複雜度,就有了後面幾種 mode,基本就是利用前一段加密過程所產出的東西來當作這一段的資料之後再加密。




接著介紹 Android 的儲存機制,Android 的儲存機制有 Shared Preferences, Internal Storage, External Storage, SQLite databases, Network connection。Shared Preferences 實體是 .xml 檔,真正的位置是在 /data/app/app 的資料夾下,這裡說可以設為 MODE_PRIVATE, MODE_WORLD_READABLE, MODE_WORLD_WRITABLE, MODE_MULTI_PROCESS。Internal Storage 的真正位置跟 Shared preferences 一樣,只是就不限於 xml。External Storage 則是在 SD Card 上。SQLite database,列出來的意思不知道是什麼,實際上這取決於放在哪裡。Network connection 的話,就是連線,一般最好就是用 SSL。列出機制以後,就是一堆範例程式。
Shared preference 是用 getSharedPreferences();Internal Storage 是用 context.openFileOutput()/context.openFileInput() 直接開檔做讀寫;SQLite Database 則要建立類別繼承 SQLiteOpenHelper ,複寫必要的函式以建立資料表格、做 CRUD 。作者是說,一般直接讀寫的情況比較少,他自己是都用 shared preference / sqlite database 比較多,操作比較方便。
章節最後是綜合應用,作者建立了一個 KeyManager 用來存放 key,Crypto 則用來作加解密:
// Key Manager
package net.zenconsult.android.crypto;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import android.content.Context;
import android.util.Log;
public class KeyManager {
private static final String TAG = "KeyManager";
private static final String file1 = "id_value";
private static final String file2 = "iv_value";
private static Context ctx;
public KeyManager(Context cntx) {
ctx = cntx;
}
public void setId(byte[] data) {
writer(data, file1);
}
public void setIv(byte[] data) {
writer(data, file2);
}
public byte[] getId() {
return reader(file1);
}
public byte[] getIv() {
return reader(file2);
}
public byte[] reader(String file) {
byte[] data = null;
try {
int bytesRead = 0;
FileInputStream fis = ctx.openFileInput(file);
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
byte[] b = new byte[1024];
while ((bytesRead = fis.read(b)) ! = -1) {
bos.write(b, 0, bytesRead);
}
data = bos.toByteArray();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "File not found in getId()");
} catch (IOException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "IOException in setId(): " + e.getMessage());
}
return data;
}
public void writer(byte[] data, String file) {
try {
FileOutputStream fos = ctx.openFileOutput(file,
Context.MODE_PRIVATE);
fos.write(data);
fos.flush();
fos.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "File not found in setId()");
} catch (IOException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "IOException in setId(): " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}
// Crypto
package net.zenconsult.android.crypto;
import java.security.InvalidAlgorithmParameterException;
import java.security.InvalidKeyException;
import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException;
import javax.crypto.BadPaddingException;
import javax.crypto.Cipher;
import javax.crypto.IllegalBlockSizeException;
import javax.crypto.NoSuchPaddingException;
import javax.crypto.spec.IvParameterSpec;
import javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec;
import android.content.Context;
import android.util.Base64;
public class Crypto {
private static final String engine = "AES";
private static final String crypto = "AES/CBC/PKCS5Padding";
private static Context ctx;
public Crypto(Context cntx) {
ctx = cntx;
}
public byte[] cipher(byte[] data, int mode)
throws NoSuchAlgorithmException, NoSuchPaddingException,
InvalidKeyException, IllegalBlockSizeException,
BadPaddingException, InvalidAlgorithmParameterException {
KeyManager km = new KeyManager(ctx);
SecretKeySpec sks = new SecretKeySpec(km.getId(), engine);
IvParameterSpec iv = new IvParameterSpec(km.getIv());
Cipher c = Cipher.getInstance(crypto);
c.init(mode, sks, iv);
return c.doFinal(data);
}
public byte[] encrypt(byte[] data) throws InvalidKeyException,
NoSuchAlgorithmException, NoSuchPaddingException,
IllegalBlockSizeException, BadPaddingException,
InvalidAlgorithmParameterException {
return cipher(data, Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE);
}
public byte[] decrypt(byte[] data) throws InvalidKeyException,
NoSuchAlgorithmException, NoSuchPaddingException,
IllegalBlockSizeException, BadPaddingException,
InvalidAlgorithmParameterException {
return cipher(data, Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE);
}
public String armorEncrypt(byte[] data) throws InvalidKeyException,
NoSuchAlgorithmException, NoSuchPaddingException,
IllegalBlockSizeException, BadPaddingException,
InvalidAlgorithmParameterException {
return Base64.encodeToString(encrypt(data), Base64.DEFAULT);
}
public String armorDecrypt(String data) throws InvalidKeyException,
NoSuchAlgorithmException, NoSuchPaddingException,
IllegalBlockSizeException, BadPaddingException,
InvalidAlgorithmParameterException {
return new String(decrypt(Base64.decode(data, Base64.DEFAULT)));
}
}
使用的時候直接用 Crypto 即可,Crypt 內部會自動去建立 KeyManager,然後使用。

文章標籤
全站熱搜


 留言列表
留言列表
